Content:
- An important rule
- What grounding systems exist
- Place of installation of grounding when working on an electric motor
- Conclusion
An important rule
According to the PUE, the grounding of the engine is done with a separate conductor. In this case, serial connection of electric motors to the circuit is prohibited, as shown in the diagram below:

If the circuit is damaged, the electric motors connected after the break become potentially dangerous due to the lack of grounding. There is a danger of equipment failure. And the incorrect operation of protection exposes personnel to danger. Therefore, such a connection is not valid.
What grounding systems exist
Existing systems make it possible to effectively protect electric motors, other equipment and maintenance personnel in an emergency. They differ in the number of conductors and the connection scheme. The governing document is PUE Ch. 1.7. rules for electrical installations. Grounding systems differ in the connection scheme and the number of conductors.
According to the PUE, they are indicated by Latin letters:
- T - grounding;
- N - connection to neutral;
- I - isolation;
- С - combination of functional and protective wires;
- S - separation throughout the network of functional and protective conductors.
According to GOST R50571.2-94, Latin letters are assigned to zero wires. They matter:
- N - functional zero;
- PE - protective zero;
- PEN is a combination of protective and functional zero.
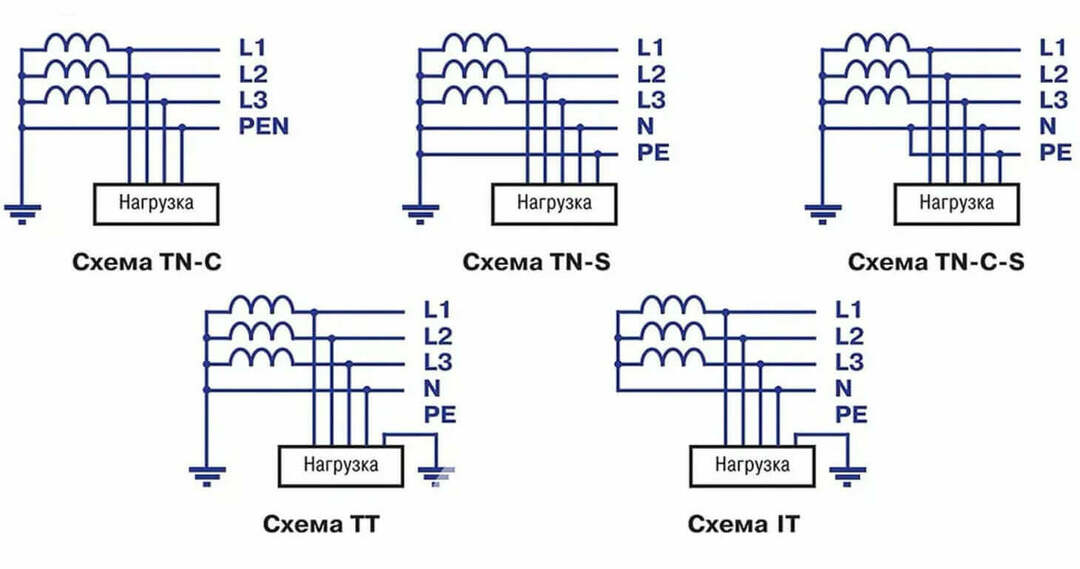
The main grounding systems are distinguished. These are TN-C, TN-C-S, TN-S, TT and IT:
- Three-phase four-wire and single-phase two-wire lines use TN-C. It is characterized by a combined neutral conductor with a grounding conductor. Those. they go from the transformer to the consumer with one conductor. This is a significant disadvantage. Used in old buildings. Not applicable in new buildings.
- TN-C-S the system differs in that the protective and neutral conductors run as one combined wire from the transformer to the switchboard, where they are separated. According to the PUE, an additional grounding device is installed.
- In the scheme TN-S protective and neutral conductors from the transformer to the consumer are separate wires.
- TT differs in that the substation transformer and the consumer have their own grounding system, which are not connected to each other. They are used to connect mobile electrical installations.
- IT - a feature of this system is the isolation of the neutral from earth or its connection through elements with high resistance. Allows to significantly reduce the leakage currents to the case. It is used in electrical installations operating in conditions of increased danger. For example, in an explosive area.
The circuit diagram below shows the described earthing systems.
PUE (Chapter 1.7, Part 1, General Requirements, Clause 1.7.33) obliges to ground the equipment powered from the AC mains. current with a voltage of 42 V and above, as well as DC motors with a voltage of 110 V and above, without fail okay.
The maintenance personnel must know how the grounding of the electric motor casings is carried out and why it is performed.
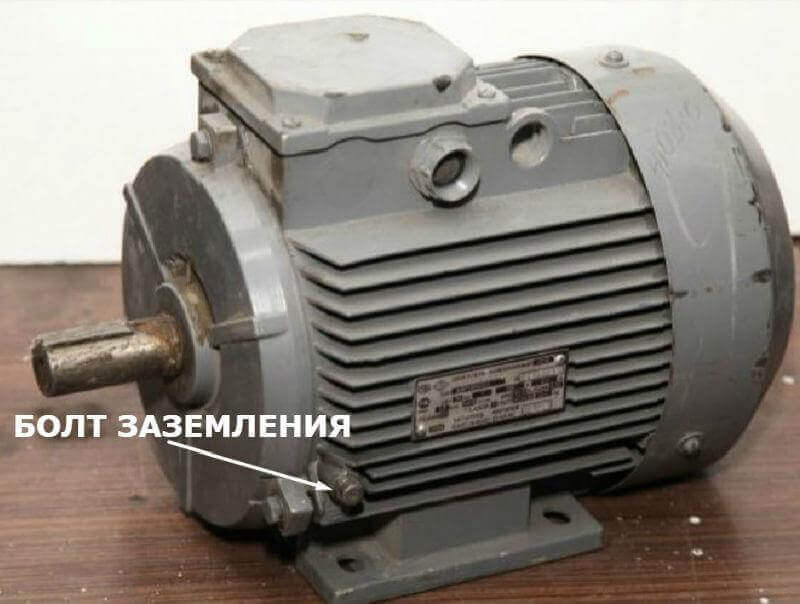
The illustration below shows the motor and the ground connection:

A missing or improperly installed grounding system will result in electric shock to service personnel or equipment failure. This is illustrated in the figure below:
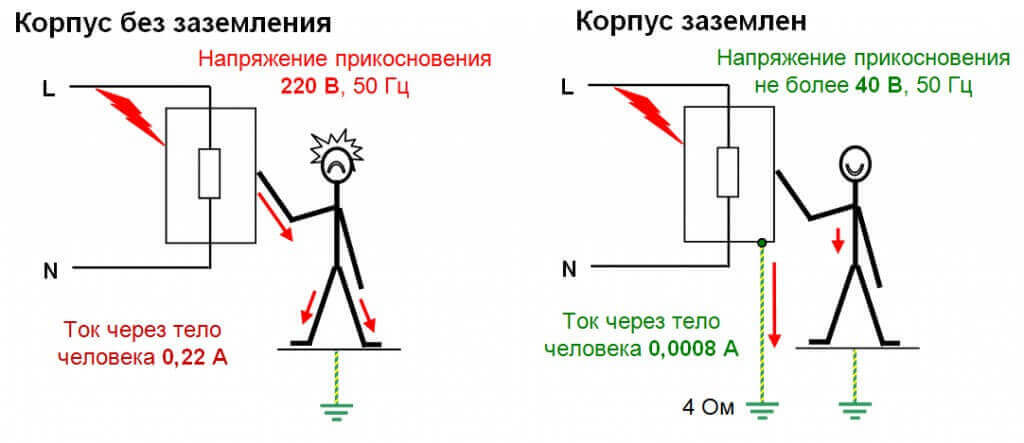
The figure shows how current flows through the human body in the presence of a ground electrode and in its absence.
In the event of a breakdown of the motor winding (figure on the right), a short circuit occurs, as a result of which a voltage appears on the case that does not exceed the permissible one. The protection circuit is activated and the equipment is de-energized.
In the absence of an earthing switch, a dangerous voltage appears on the case, which leads to the death of the maintenance personnel (figure on the left).
Electricians should know how to properly ground an electric motor. For this, the conductor is connected to a ground electrode. Only then is it connected to the equipment. It is forbidden to break this sequence.
Place of installation of grounding when working on an electric motor
It is equally important to mount portable earthing switches on the electric motor when performing repair or maintenance work. They are mounted on stationary and mobile equipment.
In this case, the service personnel must:
- Install earthing switches if work is performed on an electric drive or equipment driven by it, on which voltage may appear. The service personnel is obliged to disconnect it from the mains. Ensure protection against repeated or erroneous switching on, observing the rules of technical measures. And for two-speed motors, both winding circuits are disconnected and disassembled.
- When the power is turned off, it is allowed to install a portable earthing switch in any place, a supply cable from the switchgear, a control panel, or an assembly. This should be a visible ground.
- Before starting work on equipment that can be rotated by connected machinery (fans, smoke exhausters, pumps, etc.), valves (valves, dampers, etc.), mechanisms are locked. Or measures are taken to mechanically fix them, and the rotors of electric motors are decelerated or clutches, for example, conveyors, are disconnected.
- Appropriate signs are posted and personnel are required to use personal protective measures.
The photo below shows portable ground electrodes:
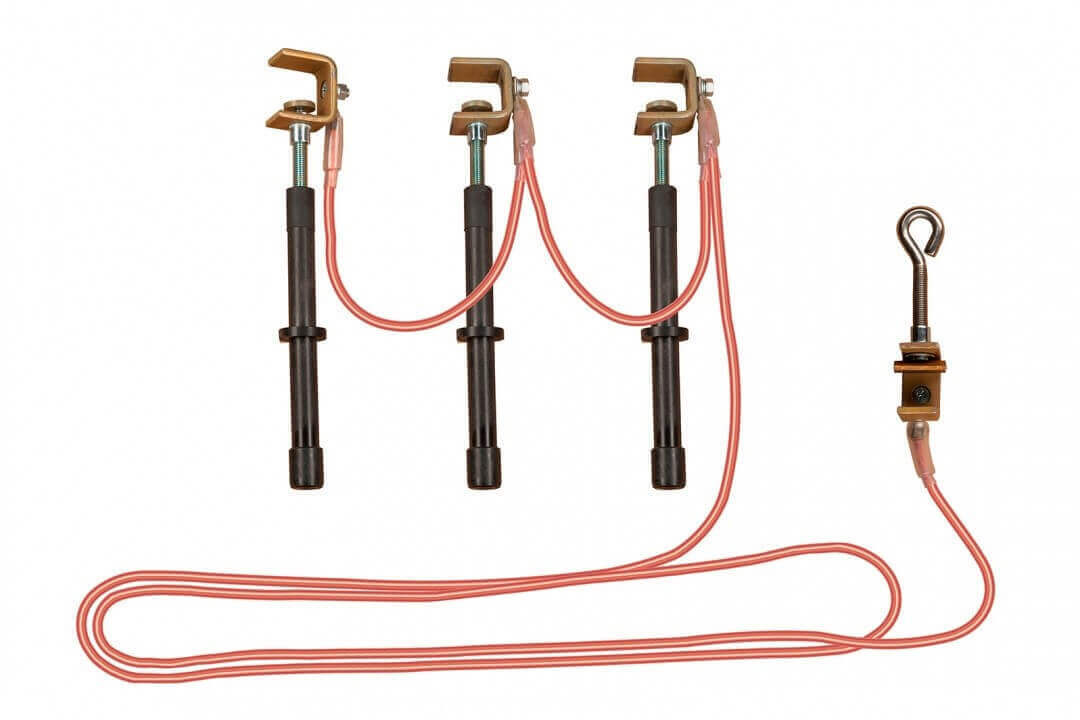
In the absence of a standard device, it is allowed to use wires as a portable ground electrode, the cross-section of which should not be less than the supply cable.
Organizations performing repair work have detailed safety instructions, in which in detail the stages of preparation of the workplace and methods of carrying out repairs, taking into account the specifics of the equipment and production.
Conclusion
The grounding of the electric motor must be in the visible area, i.e. it must be visible. This is necessary for periodic visual inspection. In dry rooms, the grounding bar is mounted on the floor.
In rooms with high humidity, the bus is installed on insulators (holders) at a distance of 10 mm from the base.
Qualified specialists are allowed to install electric motors and the ground loop. They need to know how the equipment is installed. And how to make a qualified grounding system. In addition, they must have experience and permission to carry out similar work.
Now you know how the grounding of the electric motor is carried out and what is indicated in the PUE. If you have any questions, ask them in the comments below the article!

